Breathing MOFs exhibit huge cooling potential
1st May 2022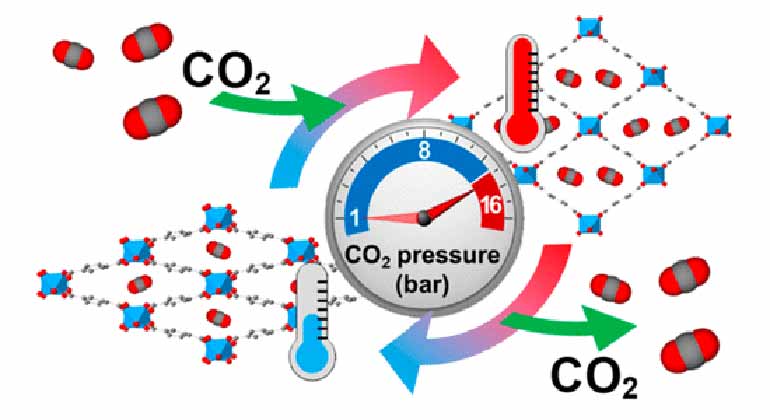
SPAIN: A team from Spain’s University of Coruña have discovered that adsorbing carbon dioxide into certain metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) can create a significant cooling effect.
Juan Manuel Bermúdez García and co-workers at the University of Coruña, who previously researched the potential for barocaloric perovskites as eco-friendly solid refrigerants, are now looking at how adsorbing carbon dioxide into certain metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) could provide greener alternatives for refrigeration.
The team has been researching MIL-53(Al), one of the class of MOFs first synthesised in 2002 that can cool down their environment as they “breathe out” CO2.
The “breathing-caloric” effect is introduced as a new term to define very large thermal changes that arise from the combination of structural changes and gas adsorption processes occurring during breathing transitions.
In regard to cooling and heating applications, this caloric effect of the MIL-53(Al) compound is said to appear under very low working pressures and in a wide operating temperature range. The large thermal changes occurred at under 16bar, a pressure which is similar to most common gas refrigerants at the same operating temperature and noticeably lower than the pressures in excess of 1000bar of most solid barocaloric materials.
The MIL-53(Al) compound can also operate in a very wide temperature range from 333K down to 254K, matching the operating requirements of most HVAC systems. According to the researchers, these findings offer new eco-friendly alternatives to the current refrigeration systems and open the door to the innovation of future cooling systems yet to be developed.
MIL-53(Al) is not seen as an isolated example. The research team anticipates that these breathing-caloric effects will appear in more MOFs and other porous materials with breathing transitions.
MOFs are crystalline porous materials that consist of a regular array of positively-charged metal ions surrounded by organic molecules and forming a repeating, cage-like structure. They have a huge internal surface area. Researchers have synthesised MOFs that feature a surface area of more than 7800m2/g, equivalent to the surface of a football field per gram of material.
A paper on the subject can be found here.
Related stories:
Barocaloric material in line for chemical prize – 30 August 2020
UK/SPAIN: A family of hybrid organic-inorganic materials that can be used as safe and eco-friendly solid refrigerants are finalists in the Royal Society of Chemistry’s Emerging Technologies Competition. Read more…







