Climate cooling bacteria found in marsh mud
20th August 2019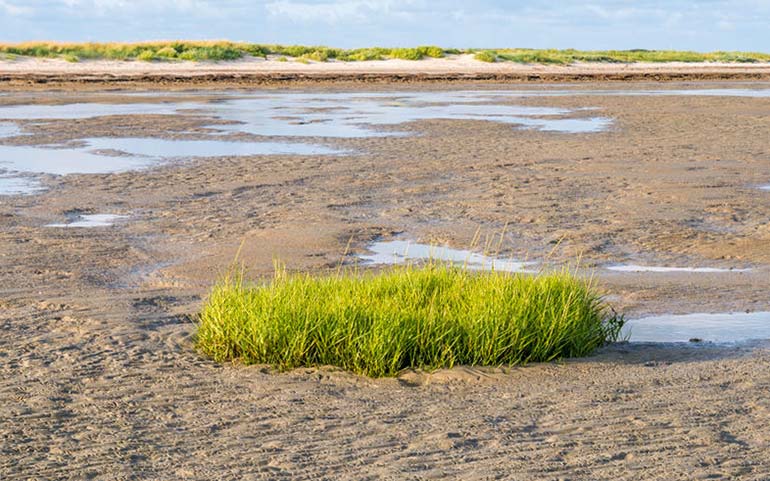
UK: Bacteria found in muddy marshes, estuaries and coastal sediment are said to be responsible for one of the Earth’s most abundant climate cooling gases.
The cooling gas is created from the break down of dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) – an important marine nutrient. Billions of tonnes of DMSP are produced annually by marine phytoplankton (microscopic plant-like cells), seaweed, corals and bacteria.
When these microorganisms break down DMSP, they release a climate-cooling gas called dimethylsulfide (DMS), which also gives the seaside its characteristic smell. Until recently, it was thought that DMSP was mainly produced in the ocean’s surface waters by photosynthetic algae.
But new research by the University of East Anglia (UEA), now published in Nature Microbiology, reveals that the molecule is produced in coastal sediment – and at much higher levels than in seawater.
Lead researcher Professor Jonathan Todd, from UEA’s School of Biological Sciences, said: “DMS is produced when microorganisms break down DMSP, and it is important because it affects atmospheric chemistry, cloud formation and potentially climate – by increasing cloud droplets that in turn reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the ocean’s surface.
“These same clouds are vital in the movement of large amounts of sulfur from the oceans to land, making the production of DMSP and DMS a critical step in the global sulfur cycle.”
The research team studied salty sediment from the North Norfolk coast at the Stiffkey and Cley salt marches. Such environments are known to produce vast quantities of DMSP and DMS, but until now it was thought that these compounds were produced by the grass, known as spartina, that grows in many such environments.
Dr Beth Williams, also from UEA’s School of Biological Sciences, said: “Working on these coastal sediments we found that DMSP levels and DMSP and DMS synthesis rates were far higher in the surface sediment than in surface seawater.
“We also found that these high DMSP levels were not dependent on the presence of Spartina, with similar levels being detected at the Yarmouth Estuary, where the plant doesn’t grow.
“Amazingly we discovered that there were as much as 100 million DMSP-producing bacteria per gram of salt marsh sediment. This supports our theory that bacteria play a very significant role in DMSP production in the sediment.
“Furthermore, we found that deep ocean sediment from the Mariana Trench also contained vastly higher levels of DMSP and DMSP-producing bacteria than the far overlying surface seawater.
“Our findings could mean that scientists have been significantly underestimating both the production of this molecule and the effect it is having in the environment.”
The study was carried out in collaboration with researchers at the Ocean University of China, the University of Auckland, Australia, and Herriot Watt University in Edinburgh, UK. It was funded by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), and Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC).